3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries by enabling the creation of complex and customized objects. One of the key factors contributing to the versatility of 3D printing is the wide range of materials that can be used. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of 3D printing materials, exploring the most common ones and their applications.
- Polylactic Acid (PLA):
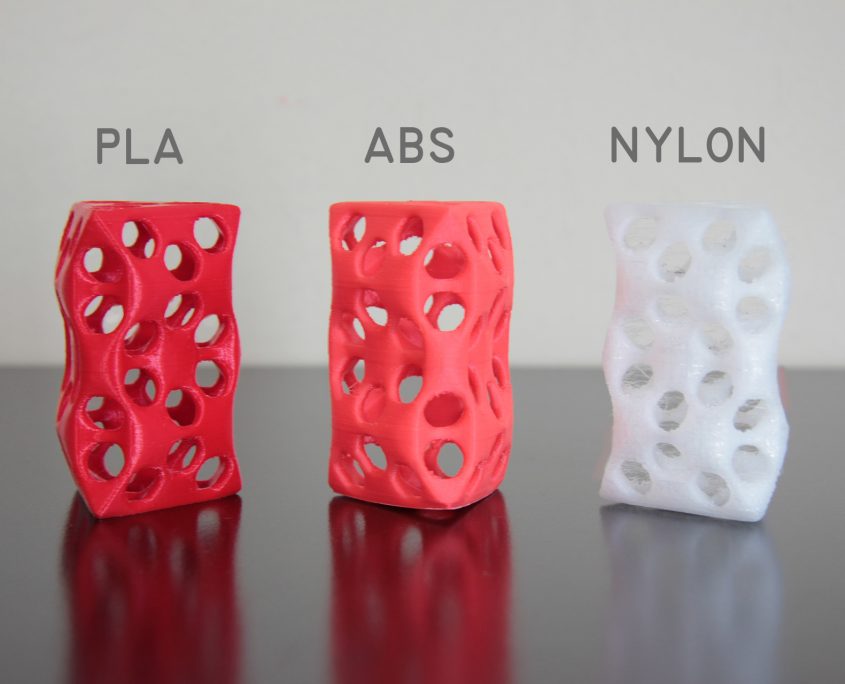
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is one of the most popular materials used in 3D printing due to its ease of use, low cost, and wide availability. PLA is commonly used for prototyping, educational purposes, and creating consumer products. Its vibrant colors and relatively low melting temperature make it suitable for creating aesthetically pleasing objects. - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
ABS is a durable and impact-resistant thermoplastic widely used in traditional manufacturing and 3D printing. It offers excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for functional prototypes, automotive parts, and electronic enclosures. ABS requires a heated print bed and a controlled printing environment due to its tendency to warp during cooling. - Polyamide (Nylon):
Nylon is a versatile synthetic polymer known for its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear. It is commonly used in industrial applications such as aerospace, automotive, and engineering. Nylon filament is favored for producing functional parts, including gears, hinges, and prosthetics, due to its excellent mechanical properties and high heat resistance. - Polycarbonate (PC):
Polycarbonate is a strong and transparent thermoplastic with high impact resistance. It is commonly used in applications that require durability and optical clarity, such as automotive components, protective equipment, and medical devices. PC's ability to withstand high temperatures and its flame-retardant properties make it suitable for demanding environments. - Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG):
PETG is a popular filament known for its durability, flexibility, and ease of use. It combines the advantages of PLA and ABS, offering good impact resistance, chemical resistance, and low shrinkage. PETG is commonly used for functional prototypes, mechanical parts, and food-safe containers. - TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane):
TPU is a flexible and elastic material widely used in 3D printing for producing objects that require rubber-like properties. It offers excellent resistance to abrasion, oil, and chemicals, making it suitable for creating footwear, phone cases, and seals. TPU's flexibility and stretchability open up possibilities for creating intricate and ergonomic designs.
Conclusion:
The world of 3D printing materials is vast and ever-expanding, offering a plethora of options for bringing ideas to life. From biodegradable PLA to high-performance polycarbonate, each material has its unique properties and applications. By understanding the characteristics of different materials, designers and manufacturers can unlock the full potential of 3D printing technology, creating innovative and functional objects across various industries.